UVE Photochemical Derivatisation
Price 240000 INR/ Piece
UVE Photochemical Derivatisation Specification
- Automation Grade
- Semi-automatic
- Material
- MS
- Voltage
- 110-215 Volt (v)
- Color
- White
- Hardness
- Yes
- Operate Method
- Semi Automatic
- Features
- Good Quality
- Usage
- Hospital & Laboratory
- Control Mode
- Manual
UVE Photochemical Derivatisation Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 01 Piece
- Delivery Time
- 5-10 Days
About UVE Photochemical Derivatisation
UV light is used in the UV-Excited or UVE photochemical derivatization process to stimulate a chemical reaction between a target molecule and a reagent. By using analytical methods like chromatography and mass spectrometry, a novel derivative molecule that is produced as a result of this reaction can be found. In particular, it is beneficial for the identification of chemicals that are challenging to identify using traditional techniques. For instance, some substances may be present in a sample in extremely small amounts or may be difficult to distinguish from other substances. In these circumstances, UVE photochemical derivatization can boost the analytical methods sensitivity and selectivity by making the target compound more detectable.


Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Environmental Instruments Category
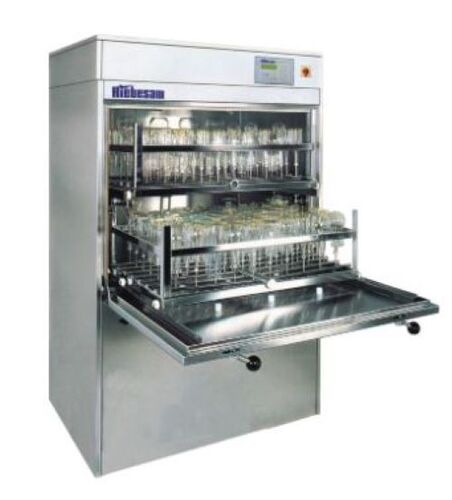
Industrial Cleaning Disinfection and Drying Machines
Price 1500000 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 01 Piece
Usage : Automatic industrial cleaning, disinfection, drying
Power Supply : 380V/50Hz, 3 Phase
Control Mode : PLC with touch screen interface
Features : Programmable cycles, HEPA filtered drying, stainless steel construction
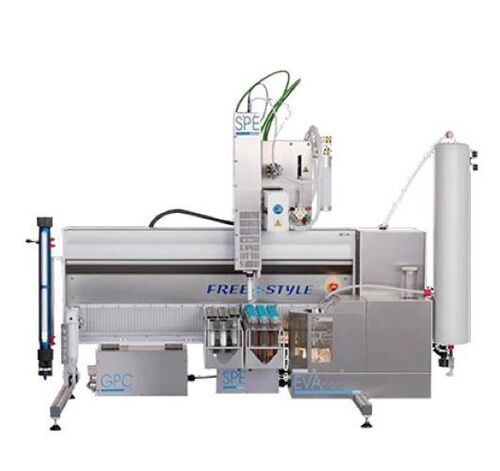
Automated GPC/SPE- Freestyle
Price 3500000 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 01 Piece
Usage : Automated Sample Preparation
Power Supply : 230 V AC, 50/60 Hz
Control Mode : Fully Automated (Touchscreen/PC Control)
Features : Automated workflow, barcode recognition, solvent selection, programmable protocols, modular design
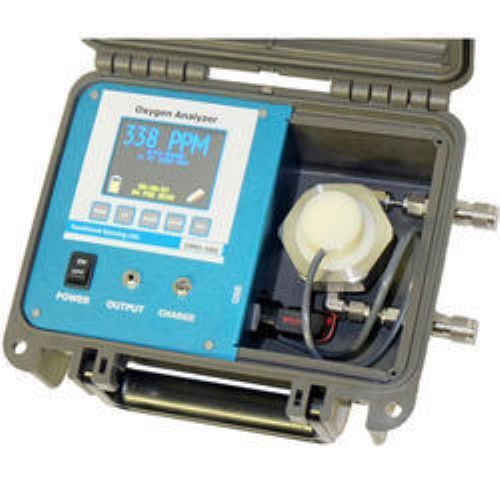
Economical Portable Oxygen Analyzer
Price 150000 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 01 Piece
Usage : Oxygen measurement in various industries including healthcare and laboratory
Power Supply : 9V Battery (standard) or DC adapter
Control Mode : Manual
Features : Lightweight, portable, compact design, userfriendly operation
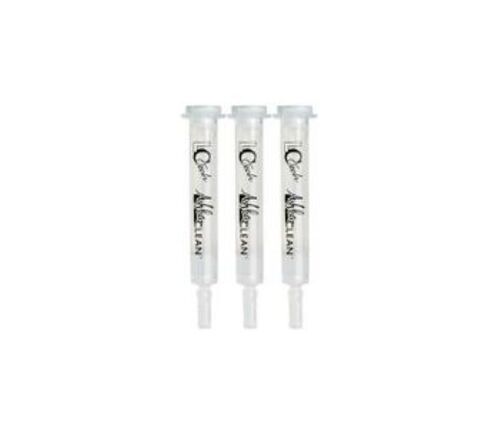
Immunoaffinity Column for Aflatoxin
Price 19000 INR / Pack
Minimum Order Quantity : 01 Pack
Usage : Laboratory
Power Supply : Manual
Control Mode : Manual
Features : Good Quality

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry