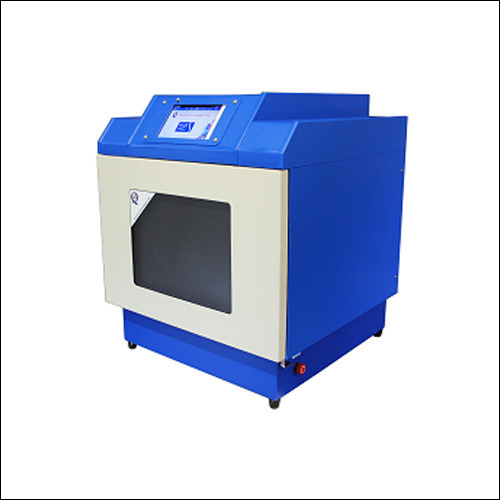
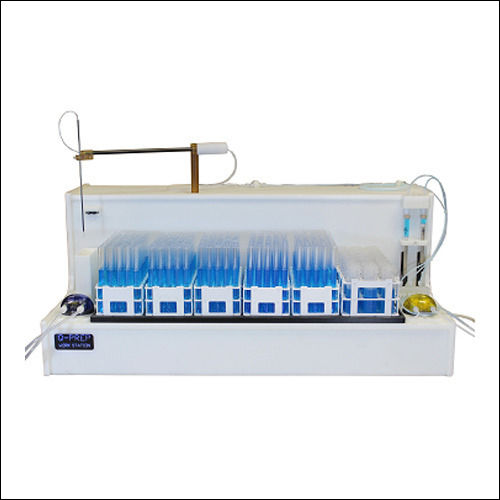
Ion Chromatography
Price 1100000 INR/ Piece
Ion Chromatography Specification
- Accuracy
- 1.5% RSD
- Test Range
- ppb to ppm (Analyte dependent)
- Humidity
- 10%85% RH (non-condensing)
- Power Supply
- 220 V / 50 Hz
- Measuring Range
- 0.01 ppm1000 ppm
- Max Height
- 480 mm
- Frequency
- 50 Hz
- Features
- Automatic eluent preparation, intelligent alarm, built-in degassing
- Display Type
- LCD Touch Screen
- Resolution
- 0.001 ppm
- Mounting Type
- Bench-top
- Interface Type
- USB, Ethernet
- Temperature
- 5C40C (Operation)
- Port Size
- Standard 1/16 inch fittings
- Application
- Water analysis, food safety, pharmaceuticals, chemical labs
- Response Time
- 10 sec
- Specimen Size
- 5 L100 L (Injection Volume)
- Automation Grade
- Semi-Automatic or Fully Automatic (Configurable)
- Number of Specimens
- 1 (per analysis)
- Equipment Type
- Ion Chromatography System
- Operating Voltage
- 220240 V AC
- Usage
- Ion concentration measurement, anion/cation identification
- Capacity
- 24-position autosampler (Optional)
- Machine Weight
- 85 kg
- Test Speed
- 0.01-20 mL/min (Pump Flow Rate)
- Test Width
- Single Channel (Standard), Double Channel (Optional)
- Test Stroke
- Up to 9999 minutes
- Control Mode
- Microprocessor Controlled
- Power Consumption
- 300 W
- Drift
- 0.05 S/cm/h
- Dimensions
- 450 360 480 mm (W D H)
- Detector Type
- Conductivity Detector (with optional UV/Vis detector)
- Software
- Data acquisition and processing software included
- Pump Type
- Micro plunger type, high-precision
- Sample Throughput
- Up to 60 samples/day
- Wavelength Range (UV Detector)
- 190900 nm (optional)
- Column Type
- PEEK, 4.6 250 mm
- Noise Level
- 0.02 S/cm
About Ion Chromatography
Different ions can be separated and examined in a sample using the separation process known as ion chromatography. Its foundation is the ion exchange concept, which calls for the selective exchange of ions between a stationary phase and a mobile phase. In ion chromatography, the sample is transported through the stationary phase by a liquid solvent, which is a column filled with ion exchange resin. The various ions in the sample interact with the stationary phase based on their charge and affinity for the resin throughout the separation process after being put into the column.
High Precision, Outstanding Accuracy
Utilizing a micro plunger type pump and microprocessor control, the system achieves an exceptional accuracy (1.5% RSD) and ultra-low drift (0.05 S/cm/h), making it suitable for trace ion analysis in even the most challenging matrices. Built-in degassing and automatic eluent preparation further enhance precision, minimizing human error.
Versatility Across Multiple Applications
Designed for water, food, pharmaceutical, and chemical analysis, this system supports measurement ranges from 0.01 ppm to 1000 ppm and resolutions as fine as 0.001 ppm. Optional dual-channel analysis and a 24-position autosampler accommodate various workflow needs, increasing sample throughput up to 60 samples per day.
Seamless Integration and Operation
Experience effortless control with the large LCD touch screen and user-friendly software for data acquisition and processing. Multiple connectivity options (USB, Ethernet) enable easy integration into laboratory environments, while automation and intelligent alarm functions help maintain stable and safe operation at all times.
FAQ's of Ion Chromatography:
Q: How does the micro plunger type pump enhance the precision of ion chromatography analysis?
A: The micro plunger type pump provides highly precise and consistent flow rates, minimizing sample variability and ensuring accurate delivery of reagent and sample solutions. This design is critical for achieving the system's low detection limits and exceptional reproducibility.Q: What types of samples and applications can this ion chromatography system handle?
A: This system is suitable for analyzing a wide range of samples such as water, food, pharmaceuticals, and chemical solutions. It is designed for the measurement of ion concentration and the identification of anions and cations, covering analytes in the ppb to ppm range.Q: When should the optional UV/Vis detector be used, and what advantage does it provide?
A: The optional UV/Vis detector, with a wavelength range of 190-900 nm, is recommended for applications where specific ions or compounds absorb ultraviolet or visible light. It improves selectivity and detection capabilities for samples containing UV-active substances.Q: Where can the ion chromatography system be installed, and what are the requirements for setup?
A: Designed for bench-top mounting, the system fits most laboratory environments. Installation requires 220-240 V AC/50 Hz power supply, non-condensing humidity (10-85% RH), and an ambient temperature between 5C to 40C. Standard 1/16 inch fittings support common laboratory plumbing.Q: What is the typical process for sample analysis with this equipment?
A: Users prepare samples and, optionally, load them into the 24-position autosampler. Precise injection volumes (5-100 L) are delivered to the column using the micro plunger pump, where separate ions are detected by the conductivity cell. Results are displayed and processed through the LCD interface and included software.Q: How does automation benefit routine operation and data accuracy?
A: Automation, such as automatic eluent preparation, sample loading, and built-in degassing, reduces manual handling, lowers risk of contamination, and standardizes procedures. This leads to increased throughput, improved precision, and more reliable data for regulatory or research purposes.Q: What support does the software provide for data acquisition and analysis?
A: The included software allows comprehensive data acquisition, real-time monitoring, method setup, and quantitative evaluation. It streamlines workflow, automates calculations, and enables secure data storage and network integration via USB and Ethernet interfaces.


Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
More Products in Environmental Instruments Category
Automated Workstation
Price Range 95000.00 - 150000.00 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Piece
Usage : Laboratory, industrial inspection
Capacity : 5000N
Automation Grade : Fully automatic
Microwave Digestion System
Price Range 95000.00 - 150000.00 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 1 Piece
Usage : Laboratory sample digestion
Capacity : 6/12 vessel rotor
Automation Grade : Fully automatic
Ultra Pure Water System Evo-RO
Price 300000 INR / Piece
Minimum Order Quantity : 01 Piece
Usage : Ultra Pure Water production by Reverse Osmosis
Capacity : 30 litres/hour
Automation Grade : Fully Automatic
Immunoaffinity Columns For Ochratoxin
Price 22000 INR / Pack
Minimum Order Quantity : 01 Pack
Usage : Singleuse, Laboratory Analysis
Capacity : 20 columns/box
Automation Grade : Manual

 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry